
In Python, the seed value is the previous value number implement by the generator.A pseudo-random number is a number that sorts random, but they are not really random.
Numpy random seed is used to set the seed and to generate pseudo-random numbers.
#Np random how to
#Np random code
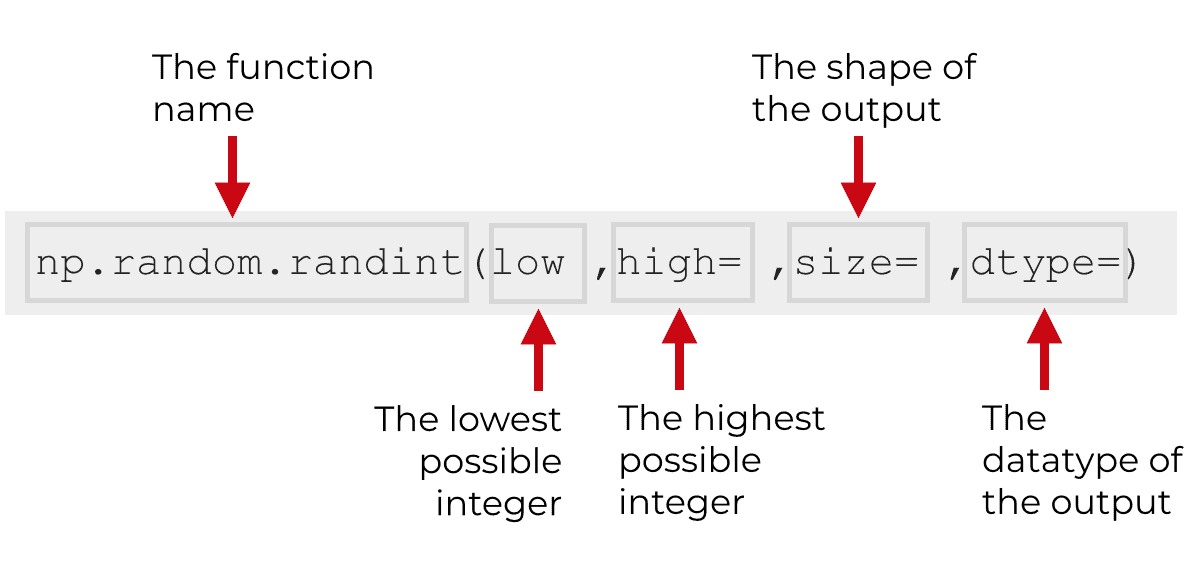
You can use the above code for Python NumPy random between 0 and 1. Np.ed(number) sets what NumPy calls the global random seed. Random(3) specifies random numbers between 0 and 1 is the size of the keyword. In this example, we will use the NumPy np.ed() function to show a random number between 0 and 1. Read: Convert string to float in Python Python NumPy random between 0 and 1 Here is the Screenshot of the following given code As you can see my output the random number is ‘5’. In the above code first, we will import a random module and then use the randint() function and to display the output use the print command it will show the number between 2 to 6. Let’s take an example and check how to get a random number in Python numpy Out: It explain the ending of the range.high: It is an optional parameter and it shows the integer number to be drawn from the distribution.low: It establish the starting range and it takes only integer value as a parameter.Here is the Syntax of randint() function random.randint In Python, the randint() function always returns a random integer number between the lower and the higher limits these both limits are the parameters of the randint() function.In Python, the numpy library provides a module called random that will help the user to generate a random number.To obtain random numbers in Python we can easily use the randint() function.Here we can see how to generate a random number in numpy Python.Python numpy random Python numpy random number Here is the execution of the following given code Now use a print statement to check which number will be shown in the output. random() function, and generate an integer number ‘4’. After that, I create a variable that is ‘result’ and assign an np. In the above code first, we will import a random module from the NumPy library. Let’s take an example and check how to implement random numbers in Python import random Return: In Python it will always returns a random integer or float numbers between the lower and higher limits.Here is the Syntax of NumPy random (size=None)
#Np random generator
In Python, the random values are produced by the generator and originate in a Bit generator. Basically, it is a combination of a bit generator and a generator.It is based on pseudo-random number generation that means it is a mathematical way that generates a sequence of nearly random numbers.This module returns an array of specified shapes and fills it with random floats and integers. In Python random is a module that is available in the NumPy library.Random means something that cannot be predicted logically. The random number does not mean a different number every time. Random numbers are the numbers that return a random integer. Alternative way to check how to implement numpy random uniform function in Python.Another way to check how to use the random normal functions in Python.Another example to generate a uniform sample by using the random choice() function.Python Numpy random number between 1 and 10.Python generate a random number from an array.python NumPy random number between 1 and 10.Python NumPy random between two numbers.Python NumPy random number in the range.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
